Temporary Modular Walls
Rethinking sustainable construction in occupied spaces

Occupied renovations present a persistent challenge for facility managers: how to modernize and maintain buildings while minimizing disruption, ensuring safety and supporting sustainability goals. Traditional methods of dust and debris containment, such as drywall partitions, often generate significant waste and require extended installation and dismantling time. These approaches can disrupt occupants, impact productivity and conflict with environmental, social and governance (ESG) objectives.
FMs increasingly seek solutions that balance operational continuity with environmental responsibility. The emergence of modular temporary wall systems offers an innovative, reusable approach to containment that addresses these competing priorities. These systems are already widely deployed, demonstrating measurable improvements in environmental outcomes, operational efficiency and occupant satisfaction.
Sustainable alternatives to traditional containment
Traditional drywall partitions are often considered the default choice for temporary containment, but they come with hidden costs. Beyond the direct material expense, these single-use walls contribute heavily to construction and demolition waste. Globally, construction and demolition activities account for nearly one-third of landfill waste, with a significant portion stemming from temporary, single-use partitions.
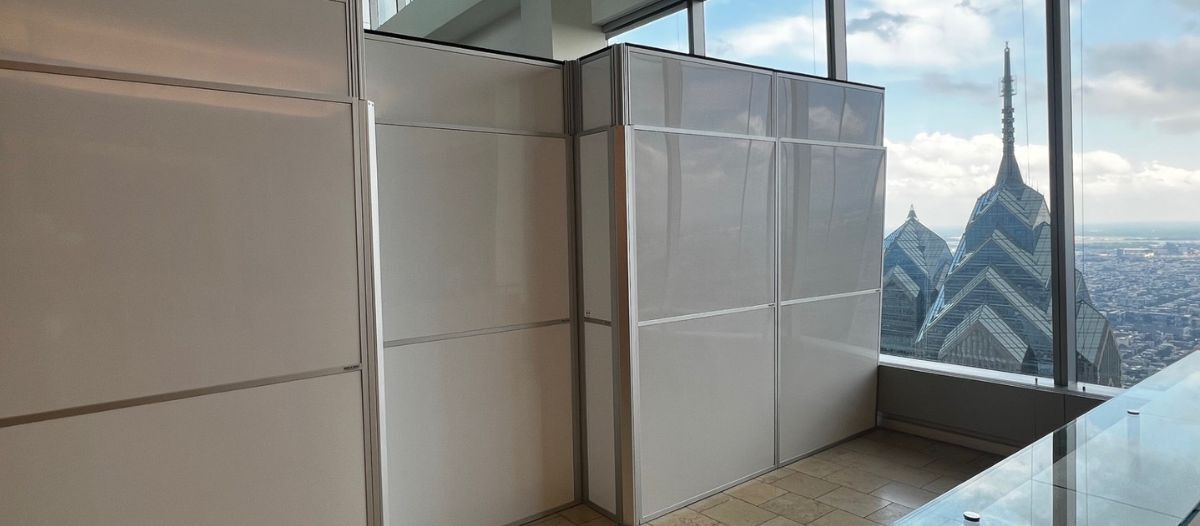
Modular temporary wall systems provide a sustainable alternative. Constructed from durable, reusable panels, these walls can be assembled, disassembled and redeployed multiple times across different projects. This reuse model significantly reduces landfill contributions and promotes a circular approach to materials management. In addition to environmental benefits, modular walls offer operational advantages. Installation and dismantling times are shorter than traditional drywall, minimizing disruption to daily building operations and enabling FMs to complete projects faster.
These systems also maintain a professional appearance, offering smooth surfaces and integrated doors or windows without compromising safety. For occupied spaces, this creates a controlled environment where occupants experience minimal interference with daily activities, improving satisfaction and reducing complaints.
Practical examples
In health care facilities, construction projects often occur while patient care continues. Modular walls can integrate with negative air pressure systems and HEPA filtration to contain dust and prevent cross-contamination. In hospitals and clinics, this approach ensures compliance with infection control standards while supporting ongoing operations. Lessons from these environments highlight the importance of planning wall layout, airflow management and staging reusable panels for rapid deployment.
Educational facilities, such as universities and schools, frequently undergo phased renovations. Modular walls allow classrooms, labs and administrative spaces to remain operational while construction occurs adjacent to occupied areas. By maintaining clean, safe zones for students and staff, FMs can minimize disruption to teaching schedules and institutional operations.
Commercial office buildings also benefit from modular containment. Corporate tenants expect minimal downtime, professional appearances and uninterrupted access to critical services. Modular walls support these expectations while allowing facility teams to conduct multiple renovation projects sequentially, reusing panels across floors and locations.
In each sector, the lessons are consistent: reusable containment reduces waste, improves occupant experience and allows FMs to measure and track sustainability metrics effectively.
Implementation & best practices
Integrating modular containment into facility operations requires careful planning. Facility managers should start by assessing renovation needs, project timelines and occupancy schedules. Identifying areas where reusable walls will provide the greatest benefit — such as high-traffic zones, sensitive environments or multiproject portfolios — can maximize impact.
Training is another critical factor. Teams responsible for installation, dismantling and storage should receive clear instructions and procedural documentation. Staging panels efficiently between projects ensures rapid deployment and minimizes idle inventory.
For FMs operating across multiple locations or countries, modular containment supports standardized operational protocols. Panels can be shipped, stored and deployed consistently, allowing global facilities to adopt a uniform approach to temporary containment while maintaining high sustainability standards.
Global relevance & broader implications
The principles of modular temporary walls are applicable globally. FMs face similar challenges: occupied spaces, sustainability pressures and operational efficiency requirements. Reusable containment panels offer a scalable solution to these challenges.
Incorporating modular walls aligns with international sustainability frameworks, including ISO 14001 environmental management, LEED certification and broader circular economy initiatives. The ability to measure waste reduction, improve occupant experience,and maintain operational continuity supports ESG reporting and enhances corporate reputation.
FMs can also leverage data collected during deployments to refine project planning, optimize resource allocation and continuously improve renovation strategies. The combination of operational efficiency and environmental stewardship positions modular containment as a forward-thinking approach to facility management worldwide.
Conclusion
Temporary modular wall systems represent a practical, globally applicable strategy for sustainable, efficient and safe occupied renovations. By shifting from disposable drywall to reusable containment, FMs can significantly reduce waste, improve project timelines and protect occupants without compromising operational goals.
Lessons from health care, education and commercial real estate demonstrate that modular containment is adaptable, measurable and repeatable. Across diverse sectors and international contexts, facility managers can integrate these systems into daily operations, supporting long-term sustainability objectives and enhancing the overall quality of building management.
As FM evolves toward environmentally responsible and operationally resilient practices, modular temporary walls provide a tangible, scalable and effective solution — transforming temporary projects into lasting benefits for both occupants and the built environment.

Biten Kothari leads Temporary Wall Systems of Metro Philadelphia, part of Temporary Wall Systems’ North American network. He collaborates with facility professionals to implement reusable containment solutions that enhance sustainability, operational efficiency, and occupant safety. With experience spanning healthcare, education, and commercial properties, he focuses on promoting environmentally responsible renovation practices and advancing best practices in facility management.
Read more on Operations & Maintenance and Project Management or related topics Space Management and Project Management
Explore All FMJ Topics